A mammogram screening is a safe, low-dose X-ray picture of the breast where two X-ray pictures of each breast are taken.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women today due to changing lifestyles, but the good news is that if detected early, it has a 90% cure rate. Mammography diagnostic is the most reliable method for detecting early and small breast cancer.
Routine screening can decrease the mortality rate by 30-35%. It can also increase the chances of breast conservation surgery. If detected early, breast cancer is curable.
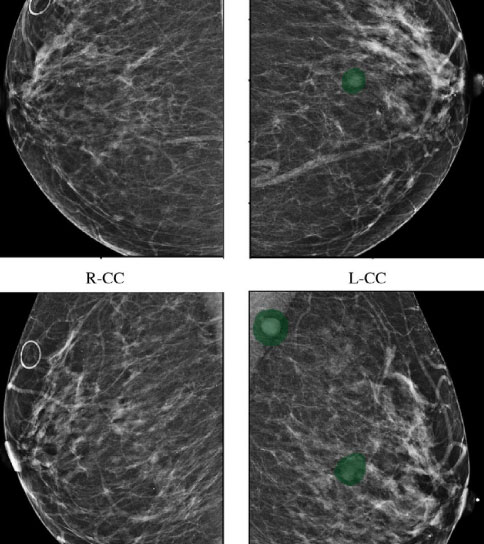
Mammography for Breast Cancer: They should do a Mammogram screening every year starting from 30 yrs of age. Examination by a physician is recommended every 3 yrs.
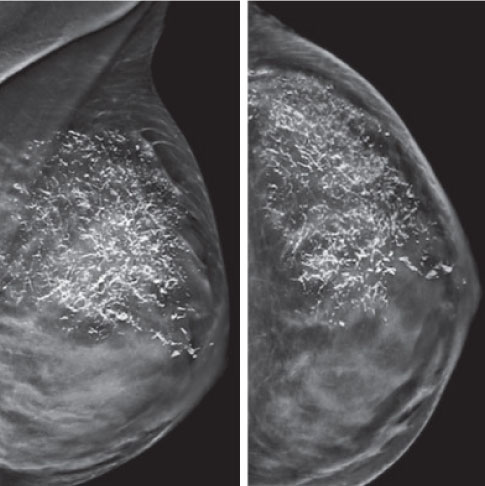
Any woman having symptoms of breast disease, i.e. lump, pain, discharge, nipple retraction or skin texture/colour changes should undergo a mammogram screening. Mammography can help to decide whether a lump is benign or malignant and can be a guide for biopsy.
In our mammography section, mammography is performed by a specially trained female radiology technologist. The breast is compressed between two plates attached to a specially designed X-ray machine. This may cause some discomfort but it is a relatively painless procedure. Compression lasts only for a few seconds and the entire procedure of mammography takes about 20 minutes. The technologist will guide you throughout the procedure and will answer all your queries.
Mammographically guides procedures like FNAC, Core Biopsies.
Breast self-examination (BSE) is a simple skill that may save your life! As implied BSE is done by women themselves, BSE should be performed each month at the same time about a week after the start of your period. Familiarity with the usual appearance and feel of one’s breast is important to notice any change such as a lump or thickening. Early discovery of a change from what is normal can be detected by BSE as early discovery increases the chances of cure. All women from the age of 20 should do regular BSE.
If you find any change in your breast, do not panic, seek your consultant’s advice immediately. Remember BSE (Breast Self-Examination) is not a substitute for regular mammograms or regular examination by a doctor.
Stay connected with Infocus Diagnostics for expert health tips, exclusive offers, and the latest updates in diagnostic care. Join our growing community and be the first to know how we’re making healthcare more accessible, accurate, and patient-focused — one post at a time.
Radiology – 7969027277
Pathology – 9099088948
helpdesk@infocusdiagnostics.com
Navrangpura 45/B, Swastik Society, Opp. Vipul Dudhiya, Stadium-Commerce Six Roads, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad-380009.