Gamma Camera
(Nuclear Medicine)
What is Nuclear Medicine?
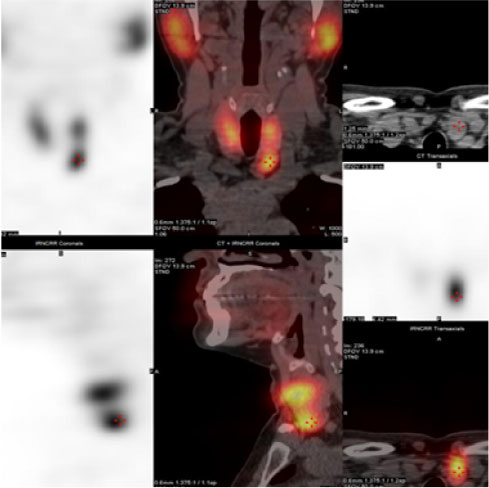
Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive material called radiotracers (radiopharmaceutical materials) to diagnose, evaluate, and treat various diseases. These radiotracers act like probes by giving signals in form of gamma rays which are captured to produce an image while scanning under a machine called a gamma camera.
Gamma cameras are commonly used in nuclear medicine procedures to visualize the heart, brain, thyroid gland, and other organs and tissues. They are also used to evaluate blood flow and to diagnose conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and infections. These images are useful to diagnose the disease or to know the function of various organs.
Nuclear medicine technology is also useful to treat certain diseases, e.g. thyrotoxicosis or carcinoma thyroid with radioactive iodine.
- Brain Perfusion Scan
- Cisternography
- Thyroid Uptake & Scan
- Parathyroid Scan
- Myocardial Perfusion / Viability Scan
- MUGA (Multigated Blood Pool Imaging)
- Lung perfusion & Ventilation Scan
- Liver Scan
- Hepatobiliary Scan
- Gastric Emptying Time
- GE Reflux
- GI Bleed
- Meckel’s Scan
- Renal Scan
- VU Reflux
- Testicular Perfusion Scan
- Scintimammography
- Lymphoscintigraphy
- Bone Scan
- Infection Imaging
- MIBG Scan
- Iodine Ablation Therapy
- Pain Palliative Treatment