An X-ray is a quick, painless imaging test that uses a small amount of radiation to create pictures of the inside of your body. It helps doctors see your bones, lungs, joints, and certain soft tissues to diagnose injuries, infections, and medical conditions.
Digital radiography (DR) is an advanced form of x-ray inspection which produces a digital radiographic image instantly on a computer. Digital X-rays produce 80% less radiation than traditional X-rays. For some types of X-ray tests, a contrast medium — such as iodine or barium — is introduced into your body to provide greater detail on the images such as a study of the uterus, genitourinary system, bowel etc. The very low radiation doses are absorbed during the imaging procedures. As a result, there are no side effects of Digital x-ray as such. However, it is best avoided in pregnancy to avoid potential harm to the unborn child.
Digital X-ray films of different parts of the body are obtained. Most commonly these are of the chest, abdomen, kidney-urethra-bladder (KUB), spine and different bones and joints.
One benefit of digital x-ray is that it produces images almost instantly, so there is no need to wait for film to be developed. This means that the results of the exam can be viewed and analyzed more quickly


They are a series of radiographs of the gastrointestinal track obtained using Barium as the dye or contrast. Barium X-rays (also called upper and lower GI series) are used to diagnose abnormalities of the GI tract, such as tumours, ulcers and other inflammatory conditions, polyps, hernias, and strictures.

An Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) or Intro Venous Urogram is a special X-Ray examination of Kidneys, Bladder & Ureters.
For an intravenous pyelogram, an intravenous line will be put in your arm or hand. A dye ( contrast material ) is injected into a vein. An IVP usually takes less than 1 hour. If your kidneys work more slowly, the test can last up to 4 hours or as required.

Fistulogram is an x-ray procedure used to view a fistula, an abnormal passage between two or more parts of your body that often drains out of your skin. A Sinogram is a similar procedure done to assess a sinus, an abnormal passage or cavity that originates or ends in one opening, often on the skin.
This test is most commonly performed on children under six months of age but is sometimes used to investigate the cause of some urinary symptoms in older children and adults (e.g. repeated infections).
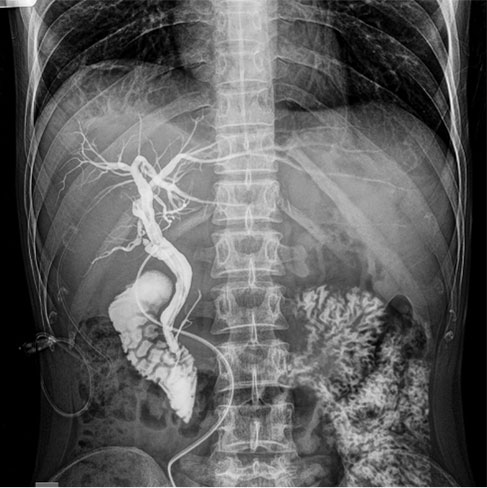
A Retrograde Urethrogram (RGU) is a diagnostic procedure performed most commonly in male patients to diagnose urethral pathology such as trauma to the urethra or urethral stricture by injecting contrast (Dye) in the urethra.
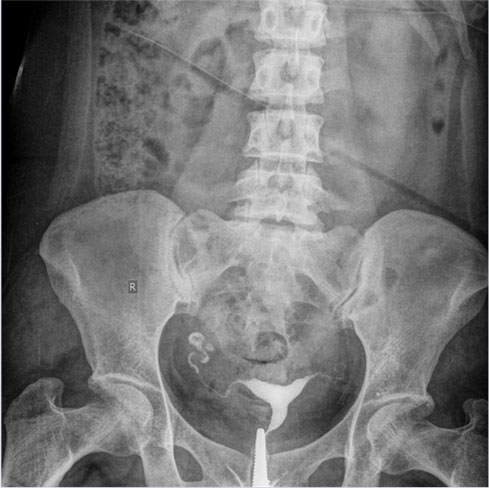
This test perform on the patients who underwent the surgical procedure for rectum cancer, sigmoid cancer or any other large intestine related disease.
INDICATIONS :
Barium Enema
A barium enema involves filling the large intestine with diluted barium liquid while X-ray images are being taken.
Preparing for Barium Enema test:
Drink clear liquids the day before the examination.
These measures are done to empty the large intestine, as any residue (feces) can obscure the image. However, a barium
A rectal tube will be inserted into the rectum to allow the barium to flow into the intestine.
Refrain from eating or drinking after midnight on the night before the examination.
An enema or laxative may be given on the day before the test to clear feces from the bowel.
During the procedure
The patient is given a bottle of barium to drink
Barium Swallow
Barium swallow and upper GI series are used to identify any abnormalities such as tumors, ulcers, hernias, pouches, strictures, and swallowing difficulties.
Preparing for barium Swallow
Patients may be advised not to eat or drink after midnight on the night before the examination.
On the day of procedure
After the procedure
NOTE:
After any of the Barium studies, if you do not have a bowel movement for more than two days after your exam or are unable to pass gas rectally, call your physician promptly. You may need an enema or laxative to assist in eliminating the barium.
Note: Report to the anesthetist in case if you have any problems like rashes, skin redness & skin swelling, sometimes associated with nausea, vomiting, and dizziness after the procedure.
Preparation:-
After Procedure:-
A child can usually go home straight away after the test.
A child will have a 3-day course of antibiotics to prevent urine infection.
Preparations:-
After Test:-
Patient can return to normal activities after this test. Patient may feel little discomfort upto 24 hours & urine may be little pink in colour.
How should I prepare?
Tests required before undergoing this procedure:- Haemoglobin, CBC, HIV, HBsAg
What will I experience during and after the procedure?
This exam should cause only minor discomfort.
You may have some slight discomfort and cramping when the doctor places the catheter and injects the contrast material, this should not last long.
There may also be slight lower abdominal pain or dull ache, this should be minimal and brief.
Most women experience vaginal spotting for a few days after the exam, this is normal.
Stay connected with Infocus Diagnostics for expert health tips, exclusive offers, and the latest updates in diagnostic care. Join our growing community and be the first to know how we’re making healthcare more accessible, accurate, and patient-focused — one post at a time.
Radiology – 7969027277
Pathology – 9099088948
helpdesk@infocusdiagnostics.com
Navrangpura 45/B, Swastik Society, Opp. Vipul Dudhiya, Stadium-Commerce Six Roads, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad-380009.