3D-4D Sonography
/ Colour Doppler
Ultrasound
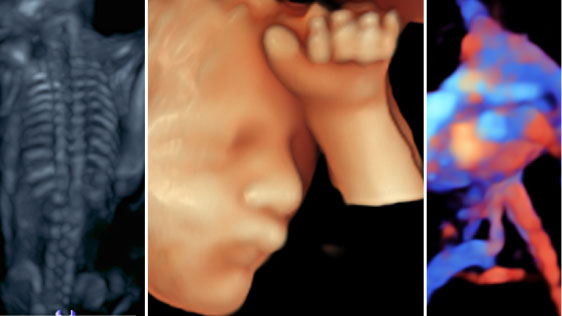
What is 3D-4D
Sonography?
Ultrasound scans/sonography works on the principle of sound reflection. It generates high-frequency sound waves to create images in 2D, 3D and 4D. The images can be viewed as pictures on a video screen/monitor.
- The standard 2D ultrasound, more commonly used in routine ultrasound of body parts, other than gynec and obstetric purposes, shows a black and white picture on a screen.
- 3D and 4D ultrasounds are widely used in obstetric practice. A 3D ultrasound creates a different perspective by merging a series of 2D images taken from various angles into a composite to form a 3D picture.
- 4D ultrasound is different from a 3D ultrasound because it adds the dimension of time, providing a live video of the baby in action: kicking, stretching, yawning, and sucking thumb.
USG Scan All Body Parts
Can help diagnose a variety of conditions and to assess organ damage following illness and to help physicians evaluate symptoms, such as pain, swelling, infection, etc.
-
- Ultrasound is a useful way of examining many of the body’s internal organs, including but not limited to the:
Heart and blood vessels, including the abdominal aorta and its major branches liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, bladder, prostate, uterus, ovaries, intestines and unborn child (fetus) in pregnant patients, eyes, thyroid and parathyroid glands, salivary glands, scrotum (testicles), breast, brain in infants, hips in infants, spine in infants.
- Ultrasound is a useful way of examining many of the body’s internal organs, including but not limited to the:
-
- Ultrasound is also used to:
Guide procedures such as needle biopsies, in which needles are used to sample cells from an abnormal area for laboratory testing. Image the breasts and guide biopsy of breast cancer. Diagnose a variety of heart conditions, including valve problems and congestive heart failure, and assess damage after a heart attack.
- Ultrasound is also used to:

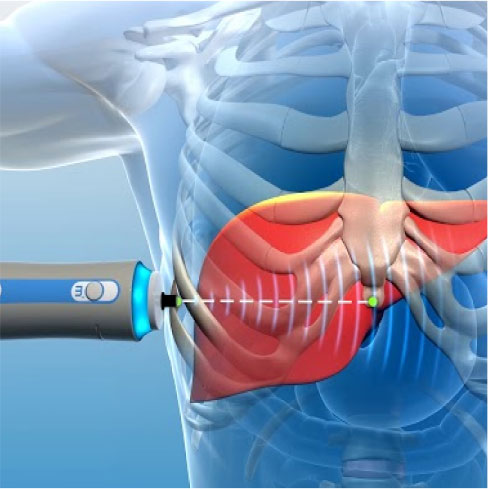
Fibroscan
This technique is used to determine fibrosis or scarring in the liver. It is used to measure liver stiffness, which is expressed in kilopascals. Essentially, the technology measures the velocity of the sound wave passing through the liver and then converts that measurement into a liver stiffness measurement; the entire process is often referred to as liver ultrasonographic elastography.
Fibroscan is a noninvasive test that can be performed at the point of care, there is no pain, and sedation is not required. Also, the test takes only 10-15 minutes to perform, it is significantly less expensive than liver biopsy, and it has not been associated with any side effects. Finally, the results of the test are instantaneous, so clinicians can use them to make decisions during patients’ visits.
Colour Doppler Sonography
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that allows the doctor to see and evaluate blood flow through arteries and veins in the body.
There are three types of Doppler ultrasound:
- Color Doppler uses a computer to convert Doppler measurements into an array of colours to show the speed and direction of blood flow through a blood vessel.
- Power Doppler is more sensitive than colour Doppler and capable of providing greater detail of blood flow, especially when blood flow is of low velocity. Power Doppler, however, does not help the radiologist determine the direction of blood flow, which may be important in some situations.
- Spectral Doppler displays blood flow measurements graphically, in terms of the distance travelled per unit of time, rather than as a colour picture. It can also convert blood flow information into a distinctive sound that can be heard with every heartbeat.
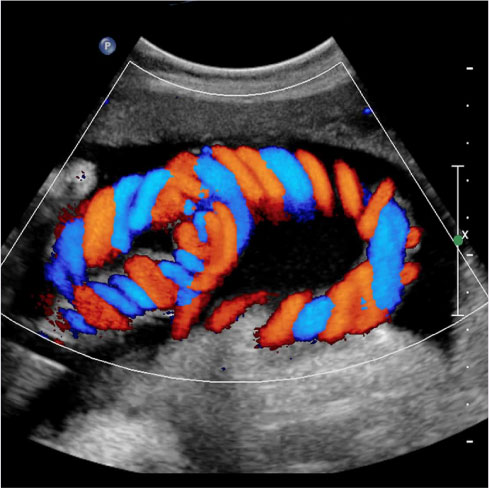
Colour Doppler Sonography In Pregnancy
Colour Doppler sonography can be used to visualize the fetus and assess its size, position, and movement. The use of colour Doppler allows the technician to see the flow of blood through the fetus’s blood vessels, which can be useful in assessing fetal well-being